Giving out a concrete answer to this question is not as straightforward as it may seem at first. Moreover, given there are so many factors at play, the answer may differ from person to person.
Sure, you can follow a general formula and find out an estimated range, but keep in mind that no battery can constantly give out an output of 12V while being paired with a device draining its charge.
A few variables must be taken into account before calculating the life expectancy of a car battery that has been linked to an inverter.
- First and foremost, you must determine the capacity and kind of your automobile battery.
- As soon as you have determined the size and variety of the battery, you will then need to evaluate how many amp-hours it possesses.
- It is also necessary to determine if the battery is a deep-cycle or a lead-acid battery.
Calculation of run time
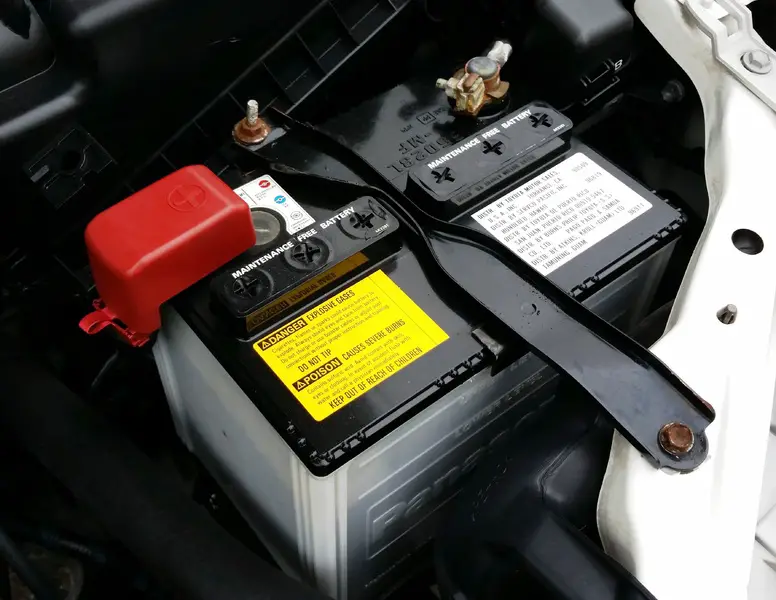

Given that you cannot have a battery with 100% efficiency without going beyond the laws of physics, it is safe to assume that the battery of your vehicle can juice up to 80-90% of its peak capacity using a 65 Watt car battery charger. On the contrary, the inverter at hand has about 72 watts. The formula that you will need to use is given below:
Multiply the battery amperes by 12 to convert the value into watt-hours. Divide the resulting number by the load watts in order to get the run-time hours. This run time can then be multiplied by 95% ( 5% accounts for the energy loss).
Going by the above rule, we can easily deduce that a 60 amp-hour battery can give us a run time of roughly 10 hours.
As the energy level of the vehicle’s battery goes down, the inverter would churn out more and more current in order to maintain a steady energy level. After all, there is no such thing as a ‘perfect battery’.
Thus, physical factors like the size of your vehicle and your inverter’s capacity to convert current should also be taken into consideration while calculation. Here is a comparison of a 12V deep cycle lead-acid battery with different AC loads :
| Appliance name | Rated load | Estimated runtime |
| Air purifier | 25 watts | 24 hours |
| Ceiling fan | 60 watts | 10 hours |
| Coffee maker | 800 watts | 45 minutes |
| Deep freezer | 25 watts | 24 hours |
| Laptop | 100 watts | 6 hours |
| Water cooler | 80 watts | 7.5 hours |
How efficient are 12V inverters?
The efficiency of a good quality pure sine wave inverter lies around 93-97%. But then, they come at a higher price as compared to their modified sine wave cousins which are on the affordable side.
Modified sine wave inverters also pose a threat to your electrical devices due to the interference caused between them.
It is crucial to note that all kinds of inverters will still have losses though, but if the inverter is loaded reasonably, then you can expect it to maintain a high-efficiency level.
The general rule of thumb suggests that you match the size of your inverter to the average expected load. Hence, any number above 40 percent is always a good measure. If the load is less than 30% then the efficiency will go down at a rapid rate resulting in heavy power losses.
Significance of battery type used
The type of your battery helps to determine the percentage of the total capacity that can be used. Normally, batteries start to lose their capacity if they undergo frequent change-discharge cycles.
Automotive batteries or SLI ( Starting, Light and Ignition) are also based on this principle only. While they can easily provide a 900 amp crank, they will not be able to handle a medium current draw for an extended time period.
The alternator in your car’s engine charges it quickly once the engine breaks its maximum power threshold. But in case you want a battery that can deliver sustained currents, then you can opt for a deep-cycle battery. The average 12V deep cycle battery can last up to 30% more than their SLI counterparts and can be discharged up to 80% of their capacity without any noticeable efficiency loss.
These batteries can be commonly seen in RVs and are often used for energy storage processes. Furthermore, it is important to note that a lithium iron phosphate battery will last longer as compared to a lead-acid battery even though you discharge it up to 95% of its capacity.
They cost more but the additional runtime is worth the price.
Speaking of inverters, what is a car power inverter anyway?
These are the devices that convert the direct current (DC) generated by your car batteries into alternating current (AC), which is the same kind of power that you find in outlets at your home linked to the energy grid.
Having a power converter allows you to plug in your appliances & gadgets and power them just as you would if you were using a regular electrical outlet in your home.
Car power inverters make use of a direct current (DC) power source, such as a car battery, to replicate or clone the alternating current energy that is supplied by the vehicle battery. Inverters that can rapidly reverse the opposition of a car battery, are now available in the market.
Types Of Car Power Inverters
Modified Sine Wave
A modified sine wave inverter, also known as a quasi-sine wave inverter, produces a waveform that is more similar to a square wave but with one additional step.
An inverter with a modified sine wave will operate well with the vast majority of equipment, but the efficiency and power of some of that equipment will be decreased.
Because of the way the modified sine wave inverter is constructed, these inverters are often more inexpensive than their pure sine wave equivalents in terms of cost. It is possible that these kinds of inverters are the best option for bigger projects that need less efficient electricity.
Pure Sine Wave
In the case of your local utility provider and certain pure sine generators, a pure sine wave is what you’re looking for. A significant benefit of using a pure sine wave inverter is that all of the equipment that is now available on the market is intended to operate with a pure sine wave as its output.
This ensures that the device will operate in accordance with its full specifications. Pure sine wave inverters have the problem of being the most costly of the inverter types, which is one of its major drawbacks. Despite this, they outperform all other kinds of inverters, regardless of the application in question.
Do you really need one?
Anyone who spends a significant amount of time on the road can profit from the use of an inverter of some kind. These gadgets are particularly helpful on lengthy road journeys when camping, for business travelers, over-the-road truck drivers, and for a variety of other uses.
Mobile phones and laptop computers can be powered by 12v accessories that can be plugged directly into a cigarette lighter or other accessory ports on the vehicle. An inverter, on the other hand, is required for every piece of electrical equipment that needs an alternating current input. Some of the gadgets that can be powered by a vehicle inverter are as follows:
- Televisions, DVD and Blu-ray players, and other electronic devices
- Systems for playing games
- Catalytic heaters
- Power tools
Things to keep in mind when using an inverter
- Installation of the inverter inside the engine chamber of the vehicle is not advisable due to the possibility of water or acid contamination. Leaving it there can result in excessive heat under the hood of the vehicle as well as a spark in the inverter by itself.
- An inverter should always be mounted on a horizontal surface.
- Make sure that the inverter is turned off if it’s near any heating vents or other sources of heat. Even exposure to direct sunlight is not recommended. The temperature must be between 50 and 80 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Keep your power inverter dry and avoid exposing it to rain or other forms of water. Make certain that you are not wet while using the equipment, since this may result in serious injury or death.
- Keep the inverter properly ventilated and away from any combustible objects. It should also be kept away from children.
Additional tips
When using a deep cycle battery to power the inverter, start the engine every 30 to 60 minutes and allow it to run for 10 minutes to recharge the battery between each start.
Using the same battery that you use to power your vehicle or truck to power your inverter is not recommended when the inverter will be running appliances with high continuous load ratings for long periods of time.
For cars and trucks, if the battery is used for a long period of time, there is a possibility that the voltage of the battery may be depleted to the point where the battery will not have enough reserve power to start the vehicle.
A second deep cycle battery for the inverter (which should be placed near the inverter) that is connected to the primary battery is a good option in these circumstances. Installation of a battery isolator between the batteries is strongly advised.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Is it okay to keep my inverter running all the time?
One of the most important reasons to switch off your inverter while not in use is that it is a significant drain on your battery’s capacity. When left on, it may rapidly deplete the battery of an RV.
- Can an inverter power a house?
An inverter can easily power a house. Power inverters are available in a variety of sizes, with the most common being 5 to 20kW. The typical house in the United States uses about 30kWh per day, which is equal to an average power demand of 1.25kW or 12500 watts.
- What is the purpose of a power inverter?
A power inverter is just another term for an inverter, which may also be referred to as a solar inverter. The term “power” is just an indicator that it has a high rating, rather than being utilized for specific applications such as tiny electrical gadgets.
All inverters serve the same function, which is to convert the direct current (DC) voltage from solar panels or batteries to the alternating current (AC) voltage required to run household electrical equipment.
- How big of a power inverter do I need?
The power rating of the DC supply, which is often a solar panel array, should be used as a general guideline to determine the size of the power converter. This is due to the fact that inverters are very efficient when fully loaded, but may squander a significant amount of electricity when they are loaded lightly.
Summing up
According to what we have studied above, a 12V vehicle battery should probably last 10-17 hours when connected to an inverter. Although there is a particular formula that you may follow, it will be dependent on the load and ampere-hour the battery packs.